Peripheral artery disease (PAD) occurs when arteries narrow or become blocked, reducing blood flow to the legs and feet. Typical symptoms include leg pain while walking (claudication), numbness, coldness, and slow-healing wounds.
However, not all leg pain or circulation issues indicate PAD. Many conditions can mimic PAD symptoms, including nerve disorders, vein problems, or musculoskeletal issues. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatment or delayed care, which may worsen long-term outcomes. Understanding what can be mistaken for PAD helps patients seek proper evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and effective management.
Let’s see the details-
What can be mistaken for peripheral artery disease/Conditions That Can Mimic PAD?
Several health conditions can produce symptoms similar to peripheral artery disease, making diagnosis challenging. Identifying the correct underlying cause is essential for effective treatment and preventing complications.
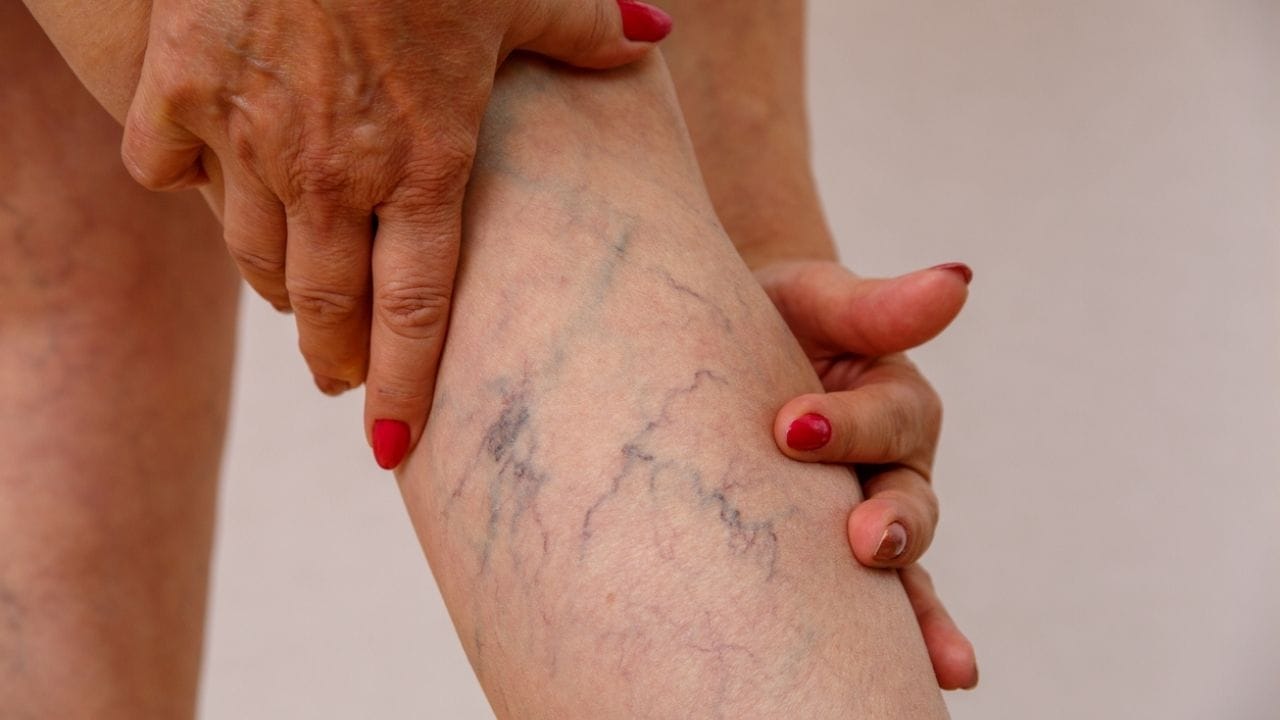
Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Patients with chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) may experience leg swelling, aching, or skin discoloration, similar to PAD. Unlike PAD, symptoms often worsen at the end of the day and improve with leg elevation.
Nerve-Related Issues
Peripheral neuropathy, often caused by diabetes, can produce numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the legs, which can be confused with PAD-induced ischemic pain.
Musculoskeletal Problems
Spinal stenosis or lumbar disc disease may cause leg pain during walking or standing, mimicking claudication symptoms. Pain is usually relieved by sitting or bending forward, which helps differentiate it from PAD.
Vein-Related Conditions
Varicose veins or spider veins may cause discomfort, visible veins, or mild swelling. These vein problems can sometimes be misinterpreted as PAD, especially in patients with coexisting arterial disease.
For patients with visible vein issues that could mimic PAD, blue light laser therapy for spider veins is an advanced treatment option to restore vein function and relieve symptoms. This non-invasive procedure targets superficial veins and can improve circulation in the affected area.
Diagnostic Approaches
Accurate diagnosis is critical to distinguish PAD from other conditions that may mimic its symptoms. A thorough evaluation helps guide appropriate treatment and prevents misdiagnosis. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI): This simple, non-invasive test compares blood pressure in the ankle with that in the arm to determine the severity of arterial blockage. A lower ratio indicates reduced blood flow, which is suggestive of PAD.
- Doppler Ultrasound: This imaging technique uses sound waves to visualize blood flow in arteries and veins. It can identify areas of narrowing or blockage and differentiate arterial problems from venous insufficiency.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: For patients with numbness, tingling, or burning sensations, these tests assess peripheral nerve function and help rule out neuropathic causes that may mimic PAD symptoms.
- Clinical Examination: A healthcare provider examines the legs and feet for swelling patterns, skin color changes, ulcers, hair loss, or weak pulses. Specific patterns of skin changes, temperature differences, and the location of pain can help distinguish PAD from venous or musculoskeletal issues.
- Advanced Imaging: In some cases, CT angiography or MR angiography may be used to provide detailed images of blood vessels, especially if surgical intervention is being considered.
- Functional Tests: Exercise treadmill tests or walking assessments can help identify claudication and evaluate the functional impact of arterial disease compared to musculoskeletal or neuropathic causes.
Together, these diagnostic approaches allow physicians to accurately identify PAD, rule out conditions like chronic venous insufficiency or nerve-related disorders, and tailor treatment plans for optimal patient outcomes. For patients with suspected vein-related issues, how to select a spider vein treatment cosmetic procedure can also be considered to improve symptoms and overall leg health.
Treatment Options for Mimicking Conditions
The management of conditions that mimic peripheral artery disease (PAD) depends entirely on the underlying cause, as each condition requires a specific approach. For patients with chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), the focus is on improving venous return and reducing leg discomfort. This can be achieved through compression therapy using stockings, regularly elevating the legs, and engaging in low-impact exercises such as walking. In more severe cases, minimally invasive procedures like vein ablation or sclerotherapy may be performed to close malfunctioning veins and restore proper circulation.
Peripheral neuropathy, often caused by diabetes or nerve damage, requires management of the underlying condition while alleviating symptoms. Blood sugar control is crucial for diabetic patients, while medications such as gabapentin or pregabalin can help relieve nerve pain. Physical therapy may also be recommended to improve mobility, reduce discomfort, and strengthen affected muscles.
Musculoskeletal causes, such as spinal stenosis or lumbar disc disease, can mimic PAD-related claudication. Treatments typically include physical therapy, posture correction, pain management, and, in severe cases, surgical intervention to relieve nerve compression.
Vein-related issues, including varicose veins, spider veins, or superficial vein inflammation, can produce pain, swelling, and visible veins that are sometimes mistaken for PAD symptoms. Conservative management strategies include compression therapy, lifestyle modifications, and leg elevation. For persistent or severe vein problems, minimally invasive procedures such as laser therapy or sclerotherapy can improve circulation and the overall appearance of the legs.
Other general interventions may involve lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing, and using medications to reduce inflammation or swelling. In rare or severe cases, surgical procedures may be required.
By focusing on the specific condition, patients can experience meaningful symptom relief, prevent further progression, and maintain overall leg and vascular health.
N.B: Treatment varies by cause: CVI (compression, exercise, procedures), neuropathy (medication, therapy), musculoskeletal (therapy, surgery), vein issues (laser, sclerotherapy, lifestyle).
When to Consult a Specialist
It is crucial to consult a vascular specialist if you notice persistent or unusual symptoms in your legs. These signs may indicate peripheral artery disease (PAD) or other vascular conditions that require prompt evaluation. Key symptoms that warrant professional assessment include leg pain that occurs during walking or even at rest, swelling that does not improve with leg elevation, non-healing wounds, skin discoloration, or cold, pale, or bluish toes or legs.
Early consultation with an experienced specialist ensures accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and helps differentiate PAD from other conditions with similar presentations, such as chronic venous insufficiency or nerve-related issues.
For expert evaluation and comprehensive vascular care, you can consult Dr. Rema Malik, who provides advanced diagnostic services, medical management, and minimally invasive procedures for patients with complex vascular concerns. Timely intervention can prevent complications, improve blood flow, and preserve mobility, giving patients a better chance for symptom relief and long-term vascular health.
Final Thoughts
While PAD is a serious circulatory disorder, several conditions can mimic its symptoms. Understanding the differences between arterial, venous, nerve, and musculoskeletal causes is crucial for accurate diagnosis. Using appropriate diagnostic tools and consulting specialists ensures proper treatment and prevents unnecessary interventions.
With targeted treatments like blue light laser therapy for spider veins and expert guidance on procedure selection, patients can manage symptoms effectively, improve leg circulation, and maintain mobility.
FAQ
What can mimic PAD?
Neuropathy, musculoskeletal pain, vein disorders, Raynaud’s phenomenon, and diabetes-related nerve damage.
Can spider veins be confused with PAD?
Yes, spider veins may cause leg heaviness or mild pain, often mistaken for PAD symptoms.
How is PAD accurately diagnosed?
Through ABI tests, Doppler ultrasound, MRA, and specialist evaluation to differentiate vascular vs non-vascular causes.
Are minimally invasive treatments effective?
Yes, procedures like laser therapy for spider veins can relieve discomfort and improve appearance safely.
References
- Hirsch, A.T., et al. (2006). ACC/AHA Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Peripheral Arterial Disease. Circulation, 113(11), e463-e654.
- Norgren, L., et al. (2007). Inter-Society Consensus for the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease (TASC II). Journal of Vascular Surgery, 45(1), S5-S67.
- American Heart Association. (2023). Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD).
- Olin, J.W., & Sealove, B.A. (2010). Peripheral Artery Disease: Current Insight. Circulation, 122(21), 2050-2060.
- Society for Vascular Surgery. Guidelines on Vein Health and Cosmetic Procedures.