Carotid stenosis is the narrowing of the carotid arteries in the neck, usually caused by plaque buildup (atherosclerosis). While it is most commonly associated with stroke risk, it can also affect blood pressure regulation, particularly when standing.
Orthostatic hypotension occurs when blood pressure drops significantly upon standing, causing dizziness, lightheadedness, blurred vision, or fainting. The carotid arteries contain baroreceptors, sensors that detect blood pressure changes and help the body respond by adjusting heart rate and vascular tone. When these sensors are impaired by stenosis, the body may not adjust blood pressure properly, leading to orthostatic hypotension.
However, now let’s see the details-
Can Carotid Stenosis Cause Orthostatic Hypotension?
Carotid stenosis occurs when the carotid arteries, the major vessels that supply blood to the brain, become narrowed, usually due to a buildup of plaque. This narrowing can reduce blood flow to the brain and, in some cases, affect how the body regulates blood pressure when you stand up.
Orthostatic hypotension is a condition where blood pressure drops significantly upon standing, causing dizziness, lightheadedness, or even fainting. Normally, your body quickly adjusts blood pressure and heart rate to keep the brain well-perfused when you change positions. However, carotid stenosis can impair these regulatory mechanisms, especially if the arteries are severely narrowed. Reduced blood flow may make it harder for the brain to receive enough oxygen immediately upon standing, which can contribute to symptoms of orthostatic hypotension.
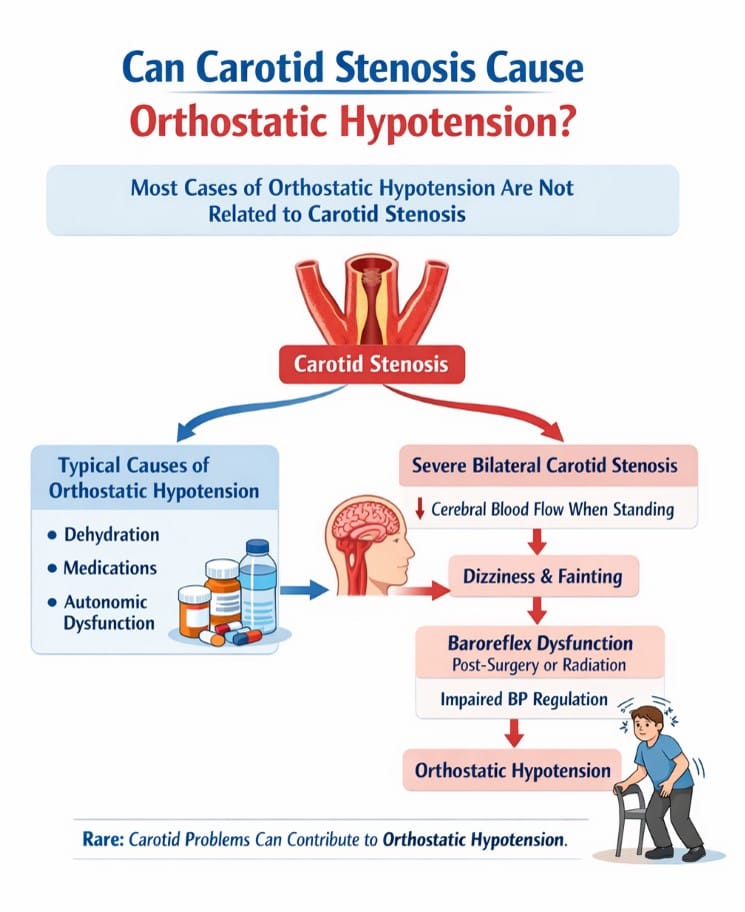
It’s important to note that carotid stenosis is not the most common cause of orthostatic hypotension. Other factors, such as dehydration, medications, heart conditions, and nervous system disorders, are usually more frequent contributors. That said, severe carotid artery narrowing can worsen symptoms in susceptible individuals, particularly older adults or those with other cardiovascular risk factors.
Evaluation often includes a thorough physical examination, blood pressure measurements lying down and standing, and imaging studies like Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography, or MR angiography to assess the degree of stenosis. Management may involve controlling cardiovascular risk factors, medications, and in some cases, procedures like carotid endarterectomy or stenting to improve blood flow.
In short, carotid stenosis can contribute to orthostatic hypotension, especially in severe cases, but it is usually one of multiple factors affecting blood pressure regulation. Prompt diagnosis and management are essential to reduce the risk of dizziness, falls, and stroke.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Patients with carotid stenosis-induced orthostatic hypotension may experience:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness when standing.
- Blurred or dim vision.
- Fainting or near-fainting episodes.
- Fatigue or difficulty concentrating after standing.
Because these symptoms can resemble other cardiovascular or neurological conditions, a thorough medical evaluation is essential.
Can Carotid Stenosis Cause Hearing Loss?
Can carotid stenosis cause hearing loss? Well, Carotid stenosis is the narrowing of the carotid arteries in the neck due to plaque buildup. While it is most commonly linked to stroke, it can also affect the inner ear and auditory pathways. Reduced blood flow to the cochlea and auditory nerve may cause sensorineural hearing loss or tinnitus (ringing in the ears).
Hearing changes can be subtle at first, often appearing as difficulty understanding speech, muffled hearing, or intermittent ringing. In some cases, patients may experience pulsatile tinnitus, where the ringing beats in rhythm with the heartbeat. These symptoms often accompany dizziness, lightheadedness, or balance issues, as reduced blood flow affects both auditory and vestibular (balance) systems.
Because these auditory symptoms can mimic common age-related hearing loss, timely evaluation by a vascular specialist or ENT doctor is essential. Early detection of carotid stenosis-related hearing issues may allow interventions as medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery- restore adequate blood flow and prevent permanent hearing damage.
Patients experiencing sudden or progressive hearing loss, especially when combined with dizziness, headaches, or vision changes, should seek immediate medical attention. Diagnostic tests may include carotid Doppler ultrasound, CT/MR angiography, and hearing assessments to determine the underlying cause.
Key Takeaways:
- Carotid stenosis can reduce blood flow to the inner ear.
- It can cause sensorineural hearing loss or pulsatile tinnitus.
- Symptoms may appear with dizziness or balance issues.
- Early medical evaluation is critical to prevent permanent damage.
Diagnosis and Expert Guidance
Diagnosis typically involves carotid Doppler ultrasound, CT or MR angiography, blood pressure monitoring, and neurological assessment.
Consulting a specialist such as Dr. Rema Malik can help assess both vascular and autonomic function, interpret imaging results, and develop a personalized treatment plan. Early intervention can prevent stroke, hearing impairment, and frequent fainting episodes.
Treatment and Management
The goal of treating carotid stenosis is to improve blood flow to the brain, prevent complications like stroke, and stabilize blood pressure, especially in cases where symptoms like dizziness or orthostatic hypotension occur. Management usually involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medications, and, in certain cases, surgical interventions.
Treatment focuses on improving blood flow and stabilizing blood pressure:
- Lifestyle adjustments -Stand up slowly, stay hydrated, and avoid prolonged standing.
- Medications -Blood pressure regulators, antiplatelets, or statins.
- Surgical interventions-Carotid endarterectomy or stenting to restore normal blood flow.
Lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in day-to-day management. Simple habits, like standing up slowly after sitting or lying down, help your body adjust to changes in position and prevent sudden drops in blood pressure. Staying well-hydrated supports overall circulation, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or straining can reduce stress on the cardiovascular system. Additionally, adopting a heart-healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular, moderate exercise all contribute to better vascular health.
Medications are often prescribed to manage risk factors and protect against further narrowing of the arteries. Blood pressure regulators help prevent excessive spikes or drops in pressure, while antiplatelet medications reduce the risk of clot formation. Statins can help lower cholesterol and slow the progression of plaque buildup in the carotid arteries, decreasing the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular events.
In cases where the narrowing is severe or causing symptoms despite medical management, surgical interventions may be necessary. Carotid endarterectomy involves carefully removing the plaque from the artery to restore normal blood flow, while carotid stenting uses a tiny mesh tube to widen the narrowed section of the artery and keep it open. Both procedures are highly effective at reducing the risk of stroke and improving blood flow, but the decision to operate is made on an individual basis after thorough evaluation by a vascular specialist.
Overall, the best outcomes are achieved when lifestyle measures, medications, and surgical options are tailored to the individual, and patients receive regular follow-up to monitor their carotid health. Early intervention and consistent management are key to preventing serious complications and maintaining healthy circulation.
Laser Vein Therapy Side Effects
Patients considering treatments for vein health should be aware of laser vein therapy side effects. Laser therapy for spider veins or varicose veins is generally safe but may cause temporary redness, swelling, bruising, mild discomfort, or rarely, skin pigmentation changes. Understanding these side effects helps maintain overall vascular health and circulation.
Prevention and Long-Term Vascular Health
Maintaining healthy blood vessels helps prevent orthostatic hypotension and other complications. Recommendations include:
- Regular exercise improves circulation.
- A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Avoiding smoking to protect the arterial walls.
- Monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol, and other cardiovascular risk factors.
Combining medical treatment with lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of fainting, hearing loss, and stroke.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can carotid stenosis cause fainting or dizziness?
Yes. Narrowed carotid arteries can impair blood pressure regulation, causing dizziness or fainting when standing.
Can carotid stenosis affect hearing?
Yes. Reduced blood flow may cause tinnitus or mild sensorineural hearing loss.
What are the side effects of laser vein therapy?
Most are mild, including temporary redness, swelling, bruising, or discomfort. Rarely, skin pigmentation changes may occur.
How can orthostatic hypotension be prevented?
Stand up slowly, stay hydrated, manage blood pressure, and maintain healthy vascular habits.
References
- British Heart Foundation. (2023). Carotid artery disease. https://www.bhf.org.uk
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Carotid artery stenosis. https://www.cdc.gov
- Cooper University Health Care. (2023). Carotid artery disease and carotid artery stenosis. https://www.cooperhealth.org
- Kozak, F. K., et al. (2019). Evaluation of cochlear and central auditory function in patients with carotid and vertebral artery stenosis. Journal of Otology, 14(3), 89-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joto.2019.06.003
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Carotid artery disease: Symptoms and causes. https://www.mayoclinic.org
- Sakallioglu, O., et al. (2018). The effect of carotid artery stenosis on hearing function. The Egyptian Journal of Otolaryngology, 34(4), 321-326. https://doi.org/10.4103/ejo.ejo_48_18
- Santos, M., et al. (2022). Improvement of tinnitus and hearing loss after carotid artery stenting: A case report. Journal of Vascular Surgery Cases, Innovations and Techniques, 8(3), 401-404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvscit.2022.06.012
- World Health Organization. (2022). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). https://www.who.int